Fortinet Acquires Next DLP Strengthens its Top-Tier Unified SASE Solution
Read the release
Cyber threats are always changing, and organizations need to stay one step ahead of these malicious attacks. Traditional cybersecurity models are too passive to keep up with evolving threats, which is why more organizations are adopting a Zero Trust model.
Zero Trust is a revolutionary framework that gives organizations a more resilient approach to safeguarding assets as they embrace digital transformation. However, it requires a paradigm shift towards proactive cybersecurity. Check out this guide to understand what the Zero Trust security model is and how to implement it in your organization.
In this article:

Traditional models assume trust within the network perimeter. However, the traditional idea of a network perimeter is obsolete in the age of digital transformation. Modern IT environments, cloud services, and the remote workforce create a vastly expanded attack surface that these traditional models are insufficient to protect.
Zero Trust is designed to secure infrastructure and data for these modern, digitally transformed environments. It operates on a simple yet powerful principle: Never trust, always verify.
This model advocates for strict identity verification, granular access controls, and continuous monitoring of every access request, regardless of its origin. Adopting a Zero Trust model improves organizational security and mitigates the risks associated with modern cyber threats.
Zero Trust has three core principles:
Zero Trust architecture improves information security by addressing the limitations of traditional security approaches. While not impenetrable, it better manages the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access than traditional approaches.

The Zero Trust security model is gaining traction in government circles, with both the United States and United Kingdom advocating for its adoption. In 2021, the White House issued an executive order directing federal agencies to implement Zero Trust strategies, citing cloud adoption and data breach risks as key drivers.
Subsequently, the U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) provided guidance and frameworks to support this initiative. Similarly, the United Kingdom National Cyber Security Centre recommended considering Zero Trust approaches for new IT deployments, particularly those involving significant cloud service usage.
This endorsement by major government entities underscores the model's relevance in modern, cloud-centric environments. As organizations increasingly rely on cloud services and face evolving cybersecurity threats, Zero Trust is becoming a preferred approach for securing new IT infrastructures.
The Zero Trust security model requires both a mindset shift and reorganizing your cybersecurity processes. Follow these tips to implement Zero Trust architecture at your organization.
Begin by evaluating your existing security measures and identifying vulnerabilities. This assessment determines any areas that require immediate attention and helps you prioritize the most high-risk resources.
Conduct a thorough review of your network infrastructure, access controls, user behaviors, and existing security protocols. Use tools like vulnerability scanners, penetration testing, and security audits to uncover potential weaknesses.
Use robust identity and access management (IAM) solutions to create secure authentication and authorization processes. This Zero Trust strategy requires strong authentication measures, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), which adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords. Single sign-on (SSO) also simplifies the login process without compromising security.
Segment your network to create isolated zones and reduce the potential spread of threats. This involves dividing your network into smaller, manageable segments, each with its own policies and security controls.
Use micro-segmentation to enforce granular access controls within these zones, ensuring that users and devices have the minimum level of access to perform their tasks.
With actionable data, you’ll be able to detect unusual patterns and potential threats more promptly. Deploy advanced monitoring tools and analytics to gain real-time visibility into network traffic.
Use tools like security information and event management (SIEM) systems, network traffic analysis (NTA) tools, and user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to collect and analyze data across your network.
Zero Trust security models emphasize protection at the device level, not just the network. All endpoints, including mobile devices and IoT devices, need appropriate security measures to ensure secure access to your organization's critical assets.
Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to monitor and protect these devices against threats. EDR tools provide continuous monitoring, detection, and automated response capabilities that identify and mitigate potential security incidents at the endpoint level.
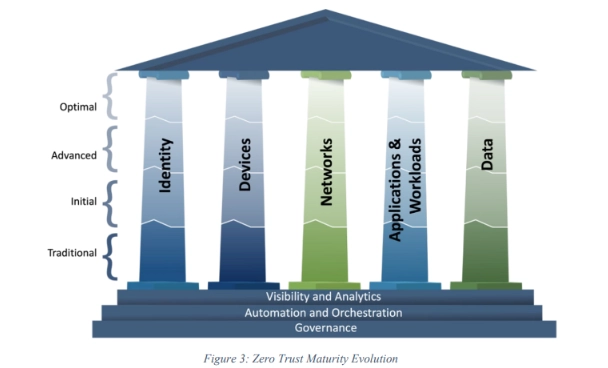
Implementing Zero Trust security is often an evolutionary process, and it's helpful to have a clear roadmap for reaching full Zero Trust maturity. The Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMMM), developed by CISA, is one of several roadmaps designed to guide organizations as they implement Zero Trust strategies and transition to a Zero Trust architecture.
The Zero Trust Maturity Model includes five pillars and three cross-cutting capabilities that reflect the seven pillars of the Zero Trust framework. Each of the five ZTMM pillars has dedicated and cross-functional security controls.
As organizations implement more of these controls with greater levels of automation, they move closer to full Zero Trust maturity. The model provides examples of traditional, initial, advanced, and optimal Zero Trust architectures within each pillar.
The Zero Trust security model is a transformative approach that safeguards data from complex threats. Implementing Zero Trust requires a mindset shift as well as a robust strategy, although the right tools make all the difference.
The Reveal Platform by Next can play a part in your Zero Trust strategy. Our cloud-native solution uses AI and ML models to keep you on the cutting edge of threat detection. Request your Next Reveal demo now.
Traditional cybersecurity models rely on perimeter defenses and assume that internal networks are secure. They trust these entities by default. A Zero Trust model, on the other hand, continuously verifies network activity, minimizes access privileges, and ensures constant vigilance. It treats every access request with suspicion, regardless of its origin.
Zero Trust works well for BYOD policies because it doesn’t assume trust based on network location. It continuously verifies all users and devices, regardless of whether they’re remote or on-site.
Zero Trust supports compliance by providing robust security measures such as continuous monitoring, strict access controls, and comprehensive auditing capabilities. These features help organizations meet various regulatory requirements for data protection, access management, and incident response.

Blog

Blog

Blog

Blog

Resources

Resources
Resources

Resources

